DAS TECHNOLOGY
Power lines and electrical grid
DAS technology offers unique advantages such as measurement over large distances, high sampling in space and time and near real-time monitoring. This is especially suitable when measuring data over long distances of overhead powerlines and underwater electric cables. The data customer base are operators and owners of infrastructure such as grids and power network companies. The most important use-cases in connection with DAS monitoring of electrical grid systems are:
Powerline monitoring:
• DAS can monitor powerlines by converting the fiber optic cable into an array of virtual microphones sensitive to acoustic energy at or in the vicinity of the line.
• It detects vibrations caused by wind, sagging lines, or mechanical stress, to be part of operators Dynamic Line Rating (DLR) and monitor conditions over time for predictive maintenance.
• Early identification of issues allows for timely maintenance, preventing power outages and ensuring grid reliability.

Fault detection and localization:
• DAS detects acoustic disturbances along overhead powerlines, such as partial discharges or arching, lightning strikes, electrical flashover/discharges and corona, line break, faulty components, unusual vibrations of towers, ice load and heavy snow and vegetation fall on lines.
• DAS monitors underwater cables for damages, faults, anchor impacts, or seismic events.
• By analyzing the backscattered light, the exact location of faults can be identified.
• Rapid fault localization enables swift responses to cable breaks, or leaks and minimizes downtime and reduces repair costs.

Security and surveillance:
• Along overhead powerlines, DAS detects unauthorized activity such as climbing in towers, theft and sabotage.
• Along underwater electrical cables, DAS detects unauthorized vessel movements, submarine activity or divers.
• This allows for enhanced security of critical infrastructure in sensitive areas.
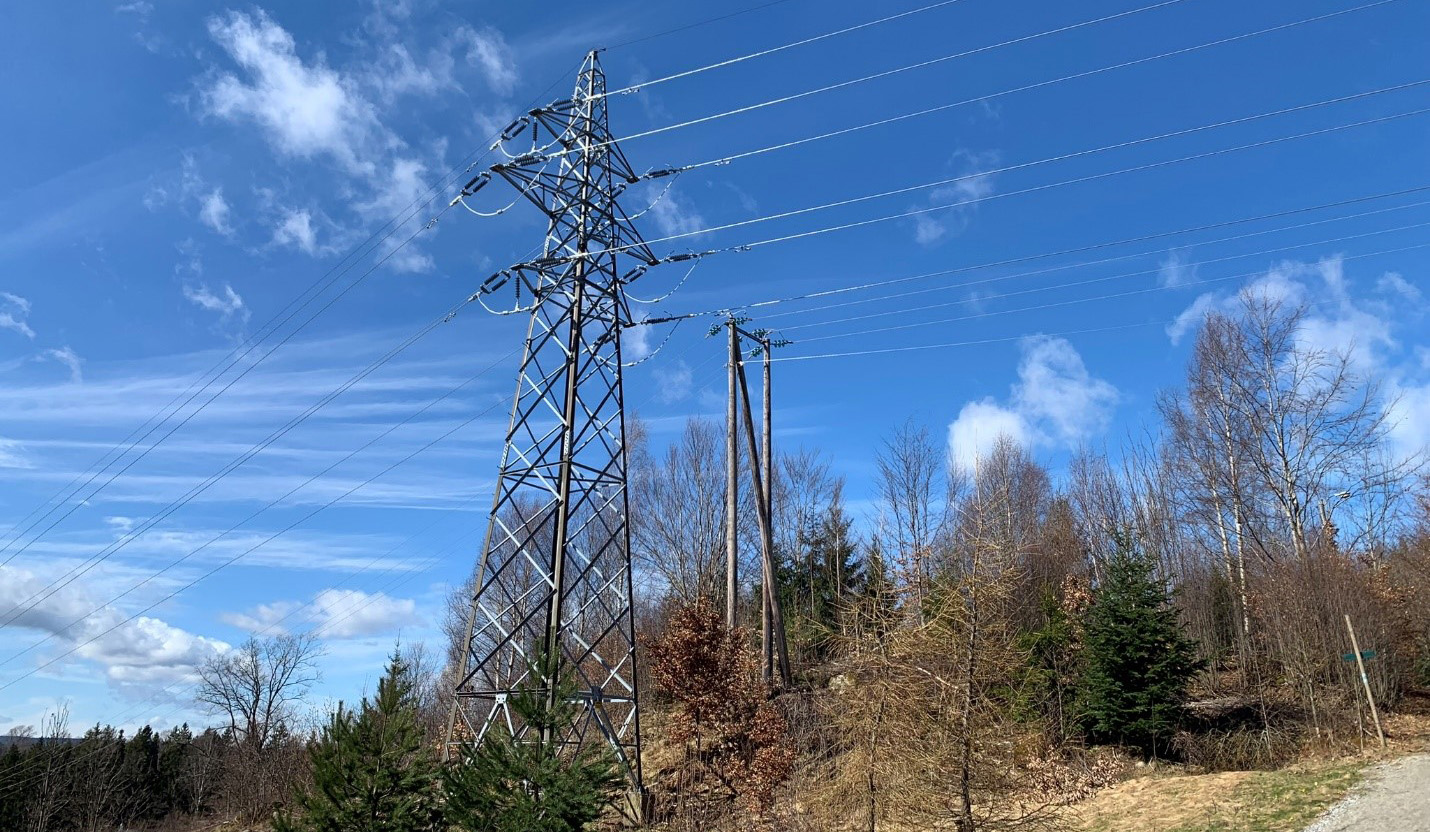

Monitoring of power lines by the utilization of OPGW, attached to the same hardware infrastructure as the electrical power lines, provides useful insight into the health of the grid and as a tool in connection of detection and classification of faults and events.

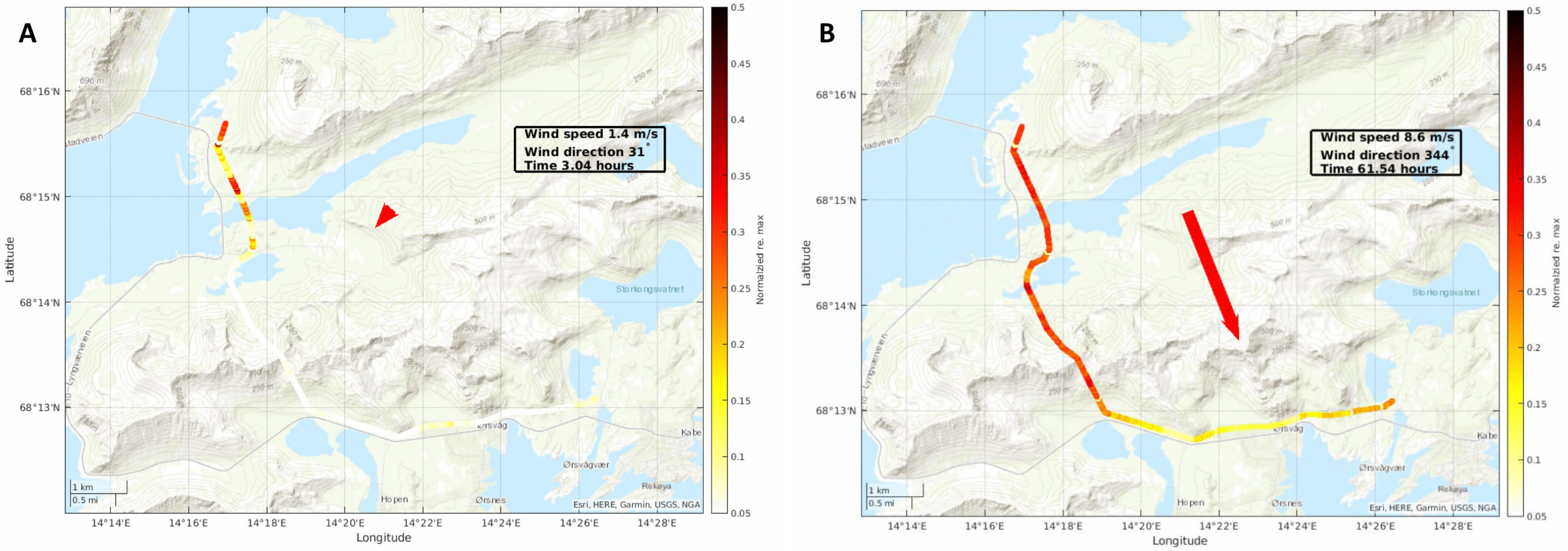
Response of a segment from the optical ground wire (OPGW) along electrical power line infrastructure for two different wind conditions.
A) Low wind from North-East providing a low RMS response along the segment. B) Higher wind from North-West direction providing a high RMS response along the line segment.
